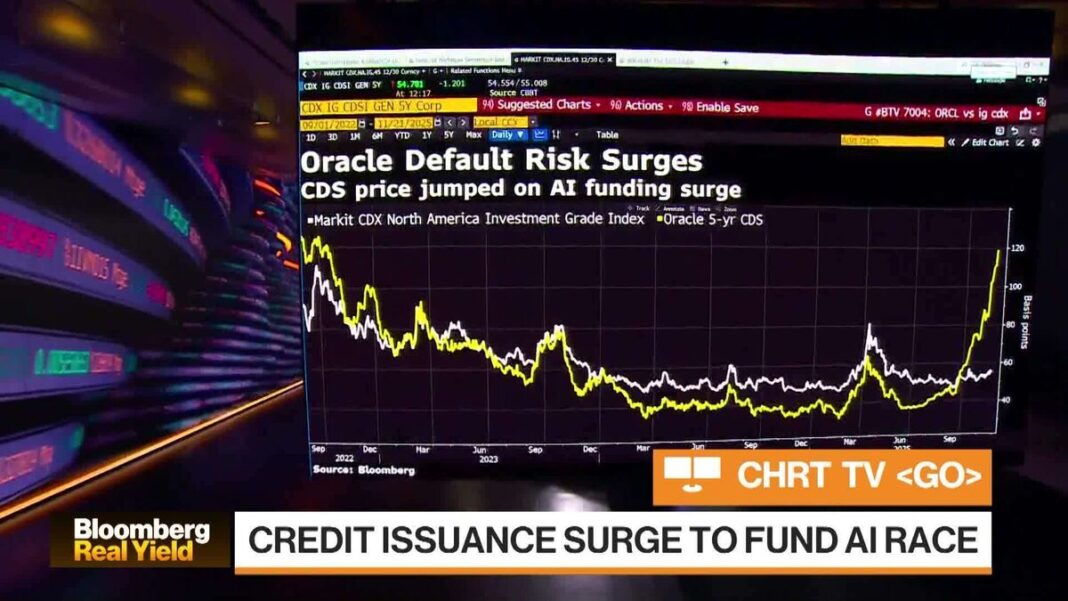
Oracle: The New Barometer for AI Risk in the Credit Market
In the rapidly evolving financial landscape, the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) has begun to reshape traditional credit markets. Recently, notable industry figures such as Leslie Falconio from UBS Global Wealth Management and Jim Schaeffer from Aegon Asset Management shared insights on Bloomberg Real Yield, highlighting Oracle’s pivotal role as a barometer for assessing AI-related risks in credit. Their discussion sheds light on the implications of AI in credit assessment and management.
The Rise of AI in Credit Markets
Artificial intelligence has infiltrated various sectors, and finance is no exception. AI technologies offer the ability to analyze vast datasets, streamline operations, and enhance decision-making processes. Credit markets, in particular, benefit from AI’s capabilities, enabling lenders to assess borrower risk with unprecedented precision. However, this transition also introduces a unique set of challenges that require careful navigation.
Oracle’s Role in Risk Assessment
Oracle is positioning itself as a key player in monitoring the credit market’s pulse concerning AI risks. By utilizing advanced analytics and cloud-based solutions, Oracle provides tools that help financial institutions evaluate creditworthiness. Falconio and Schaeffer emphasize that the integration of Oracle’s technologies allows firms to improve risk models and predict potential defaults more effectively. This advancement enhances the overall stability of credit markets, but it is not without its pitfalls.
Identifying Risks with AI Integration
Despite the benefits, integrating AI into credit assessment raises concerns. One major issue involves the opacity of AI algorithms, often referred to as the “black box” problem. As Falconio pointed out, it can be challenging for financial institutions to fully understand how AI models arrive at their conclusions. This lack of transparency can lead to inherent biases in lending practices, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities in credit access.
Regulatory Implications
The regulatory landscape is catching up to the advances in AI, and institutions must remain vigilant. Schaeffer notes that regulators are increasingly scrutinizing the algorithms used in credit risk assessments to ensure fairness and compliance with existing laws. This regulatory pressure can affect how firms implement AI technologies, pushing them to prioritize compatibility with guidelines while striving to maintain efficiency in credit evaluations.
The Importance of Data Integrity
Data quality is another crucial factor in deploying AI in credit markets. Falconio emphasizes that the information fed into AI algorithms significantly influences their output. Poor data quality can lead to misguided credit assessments, resulting in substantial financial repercussions for both lenders and borrowers. Ensuring robust data governance practices is essential for institutions looking to leverage Oracle’s technologies without compromising accuracy.
Future Considerations for Credit Markets
Looking ahead, the interaction between AI and credit markets will likely evolve, requiring ongoing adaptation and vigilance. Institutions must not only focus on harnessing the benefits of AI but also recognize the associated risks. Both Falconio and Schaeffer stress the importance of continuous monitoring and updating of risk models to reflect the changing landscape influenced by AI advancements.
Building a Safety Net
Financial institutions can establish safeguards as they navigate this new terrain. Integrating human oversight alongside AI-driven analytics can mitigate biases and enhance the robustness of credit decisions. Creating interdisciplinary teams that combine technology expertise with traditional financial acumen can foster a well-rounded approach to risk management.
The Global Context of AI Risk
Global events, such as economic fluctuations or geopolitical tensions, compound the complexity of assessing AI risk in credit markets. As Falconio and Schaeffer discuss, the interconnectedness of global finance means that risks can propagate rapidly across borders. Institutions that embrace a global perspective when leveraging AI technologies will be better equipped to manage unforeseen challenges in credit assessments.
Through this thoughtful exchange of insights, the conversation around Oracle’s role as a barometer for AI risk in the credit market is both timely and essential. As financial institutions continue to embrace AI, understanding its impacts and implications will be crucial for ensuring stability and fairness within the ever-evolving landscape of credit markets.