The Swiss National Bank and the Zero Interest Rate Policy
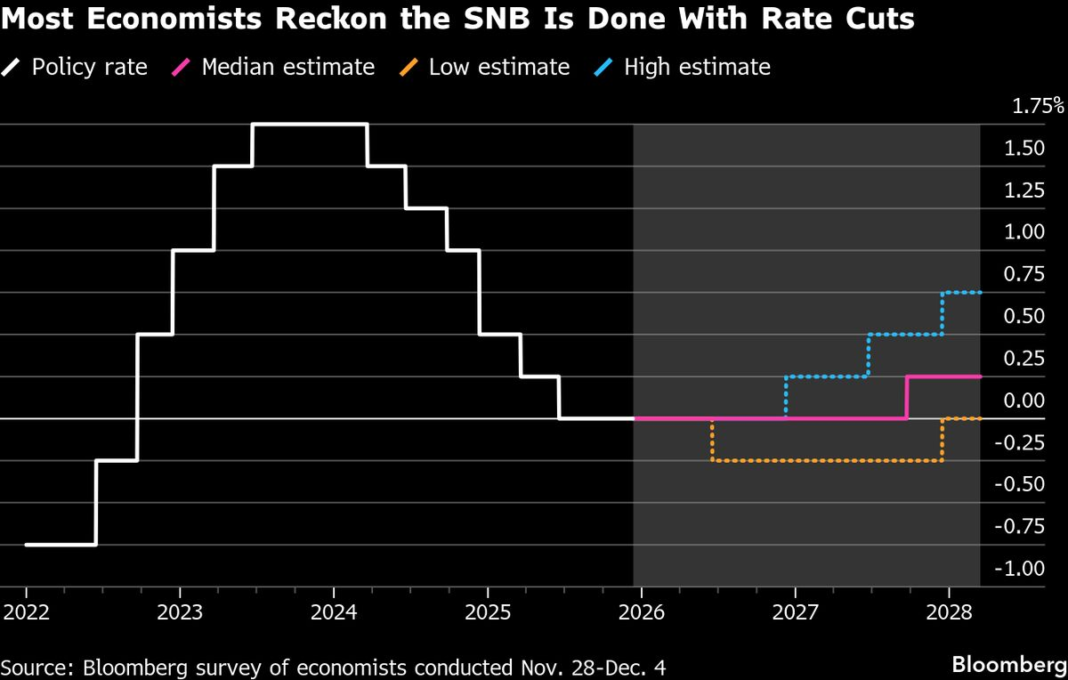
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) is often in the spotlight due to its pivotal role in the Swiss economy. Recently, anticipation has been building around its upcoming decision regarding interest rates. This decision is particularly intriguing as the SNB is expected to maintain its interest rates at zero, signaling its current stance on economic stability and growth.
Understanding the Current Economic Landscape
Before diving into the implications of the SNB’s decision, it’s essential to understand the economic environment. Switzerland has enjoyed a stable economy, characterized by low unemployment rates and inflation. However, amid global economic uncertainty, central banks worldwide are adjusting their monetary policies. The SNB’s decision to keep interest rates at zero reflects a cautious approach, prioritizing stability in turbulent economic times.
The Role of Negative Interest Rates
Negative interest rates have become a tool for some central banks, intended to encourage spending and investment by penalizing savings. The SNB was one of the first central banks to introduce this policy in 2015, aimed at preventing the Swiss franc from appreciating too rapidly against other currencies. Keeping rates at zero suggests reluctance to return to negative territory, indicating a careful calibration of economic policies to avoid unwanted repercussions.
Insights Into the Decision-Making Process
The SNB’s decision-making process is highly strategic. By maintaining zero rates, the SNB is signaling its assessment of the economic conditions both domestically and internationally. Specifically, it reflects a balance between supporting economic growth and managing inflation. Observers will be keenly watching any statements released alongside the decision for insights into the bank’s future direction.
Expectations from the Upcoming Announcement
With the SNB expected to provide clues on its threshold for returning to negative rates, analysts are eager to decode what this might mean for the Swiss economy. There may be hints regarding the conditions that would prompt such a dramatic policy shift. These could include economic downturns, significant inflationary pressures, or shifts in global economic dynamics.
The Impact of Zero Interest Rates on Consumers and Businesses
For consumers, zero interest rates can be a double-edged sword. On one hand, borrowing costs remain low, stimulating spending and investment. On the other hand, savers may find little incentive to save, leading to a potential decrease in personal savings rates. Additionally, businesses benefit from lower borrowing costs; however, they may still hesitate to invest if uncertainty looms over the economy.
Reactions from the Financial Markets
Financial markets often react swiftly to central bank decisions. While maintaining a zero interest rate is generally well-received, especially for currency stability, any hints about possible future changes can lead to volatility. Traders will be looking for clues about how the SNB might respond to an inflating economy or external shocks.
Global Implications of the SNB’s Policy
The SNB’s stance doesn’t operate in a vacuum; it significantly impacts the global economic landscape. Switzerland is home to many multinational corporations and financial institutions, and its monetary policy can influence foreign investments and currency dynamics. Other central banks may observe the SNB closely, especially those in Europe, where negative rates have become a pertinent topic.
The Path Forward for the SNB
Looking ahead, the SNB’s decision to keep rates at zero suggests a cautious strategy focused on sustaining economic growth without aggravating inflation. Analysts will be scrutinizing the bank’s future communication for any shifts in tone or strategy, as even a small change could signal a broader move in monetary policy.
In assessing the implications of the SNB’s decisions, it’s crucial to stay informed and engaged with ongoing financial news, as each announcement can ripple across markets and economies worldwide.